Using Ice and Cold for Tarantula Bites

Tarantula bites can cause discomfort and unpleasant symptoms. But, using Tarantula Bite Ice and cold therapy can help. This guide will show how ice and cold can lessen the effects of tarantula venom. We’ll also look into the latest in venom research and antidote development.
Tarantulas are not just far-off creatures; they’re moving closer to us as cities grow. Knowing how to treat tarantula bites is key to staying safe. Let’s learn how ice and cold can help in these situations.
Understanding Tarantula Bite Symptoms
Meeting a tarantula in the wild can be thrilling, but knowing about their bites is key. Tarantula venom can lead to mild to severe symptoms, based on the species and venom potency.
Identifying Venom Effects
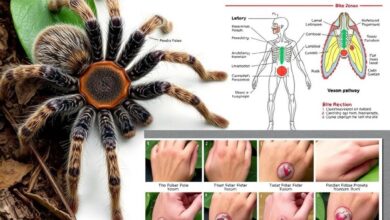
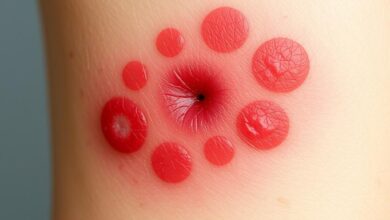
A tarantula bite can cause pain, swelling, and redness where it bites. You might also feel nausea, vomiting, and muscle spasms. How bad these symptoms are can vary. If you think a bite is serious, get medical help right away.
Recognizing Signs of Envenomation
- Pain and Swelling: The bite might hurt a lot, and the area could swell and get inflamed.
- Redness and Irritation: The bite spot might look red and irritated, with visible marks.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some people might feel sick and throw up because of the venom.
- Muscle Spasms: In bad cases, the venom could make your muscles shake or spasm.
| Tarantula Species | Venom Potency | Bite Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Poecilotheria species (Ornamental Tree Spiders) | Highly Potent | Severe pain, swelling, muscle spasms, respiratory distress |
| Aphonopelma species (North American Tarantulas) | Mild to Moderate | Mild pain, swelling, redness |
| Psalmopoeus species (Guyana Pinktoe Tarantulas) | Moderate | Moderate pain, swelling, nausea |
Knowing about tarantula venom’s effects is crucial. If you feel bad after a bite, get medical help fast. Learning the signs of a venomous bite can help you act quickly in an emergency.

Tarantula Bite Ice
Applying ice or cold therapy to the bite site right away is key. It helps reduce swelling, pain, and how much venom gets in. Quick action is vital, as the venom’s effects can worsen fast.
Importance of Immediate Ice Application
Putting ice or a cold compress on the bite area quickly can make a big difference. Cold therapy constricts blood vessels, slowing the venom’s spread. This reduces symptoms and helps with pain and swelling from the bite.
Proper Technique for Cold Therapy
- Put a cold, damp cloth or ice pack on the bite as soon as you can, ideally within the first 5-10 minutes.
- Make sure the cold isn’t touching your skin directly to avoid more harm. Use a thin towel or cloth to cover the ice pack or cold compress.
- Keep the cold therapy going for 10-15 minutes, then do it again every 1-2 hours if needed.
- Don’t use ice or cold therapy for more than 20 minutes at a time to prevent tissue damage.
By doing these steps, you can help manage the bite’s symptoms and provide important first aid. Cold therapy is a key part of emergency care for tarantula bites.
Emergency Care for Tarantula Bites
Most tarantula bites cause mild reactions. But, some need immediate medical help. If symptoms are severe or the victim is allergic to the venom, get emergency care fast. Knowing when to seek help and what to do until help arrives is key to keeping the victim safe.
Start by checking how bad the bite is. Call for emergency medical help right away if the victim has severe symptoms. These include:
- Severe pain or swelling that spreads beyond the bite site
- Difficulty breathing or signs of respiratory distress
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Dizziness, confusion, or loss of consciousness
- Signs of an allergic reaction, such as rash, hives, or difficulty swallowing
While waiting for help, here’s what you can do:
- Stay calm and reassure the victim.
- Clean the bite area with soap and water to remove venom.
- Use a cold compress or ice pack on the bite to reduce swelling and pain.
- Watch the victim’s vital signs, like breathing and pulse, and know CPR if needed.
- Don’t give any medicines or try to suck out the venom, as it can be harmful.
Knowing the signs of a severe tarantula bite and acting fast can save lives. It ensures the victim stays safe until medical help arrives.
Tarantula Species and Venom Potency
The world of tarantulas is vast and diverse, with hundreds of species. Each one has a different level of venom potency. Knowing how different tarantulas’ venom works is key to treating bites right.
Evaluating Venom Toxicity Levels
Tarantula venom can be mild or very dangerous. Some, like the Poecilotheria genus, have very strong venom. This can cause a lot of pain, muscle spasms, and trouble breathing.
On the other hand, the Brachypelma genus has less potent venom. Their bites usually cause less severe reactions.
Understanding Antivenoms
For serious tarantula bites, antivenoms are often needed. These antidotes target the venom of certain tarantulas. But, not all places have the right antivenoms, and their effectiveness can vary.
It’s important for doctors to know which antivenoms work best for local tarantulas. This helps in treating bites effectively.
Knowing about tarantula species and their venom helps people make smart choices. It guides them on when to get medical help and what treatment to use for a tarantula bite.
Advancing Venom Research and Antidote Development
Ongoing research in tarantula venom and antidote creation is key. It helps improve treatments and understand spider toxins better. Researchers aim to find the secrets of spider venom. They want to make better antidotes and treatments for tarantula bites.
Recent studies have given us new insights into tarantula venom. They show how certain compounds in the venom could help with health issues. This research opens up new possibilities for treatments.
The need for better venom research and antidotes is clear. In Switzerland, there were 104 verified spider bites. In Zimbabwe, there were 771 scorpion stings. This data shows the wide impact of venomous encounters. Researchers can use this information to find better treatments and understand the effects of venom.