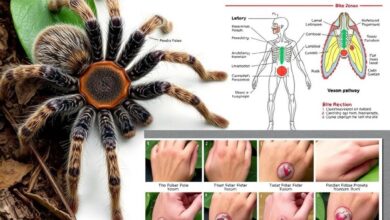
First Aid for Children after a Tarantula Bite

The thought of your child getting bitten by a tarantula can be scary. But, with the right knowledge and quick action, you can help keep them safe. What are the essential first aid steps you should take if your child falls victim to a tarantula’s venomous fangs?
This guide will cover the key first aid steps for a tarantula bite emergency. We’ll talk about the effects of the venom and how to spot a severe reaction. By the end, you’ll know how to act fast and with confidence if your child gets bitten.
Understanding Tarantula Venom and Its Effects on Children
Tarantulas are fascinating, but their venom can be dangerous for kids. It’s important to know how tarantula venom affects children. The effects can vary by species and the child’s sensitivity.
Symptoms to Watch for in Young Tarantula Bite Victims
Children bitten by tarantulas may feel pain, swelling, and redness where they were bitten. Sometimes, they might also get nausea, vomiting, or muscle spasms. Keep an eye on the child and get medical help if symptoms get worse.
Differences in Venom Potency Among Tarantula Species
Not all tarantulas have the same venom strength. Some, like the Poecilotheria, have strong venom that can cause serious reactions in kids. Others, like the Avicularia, have milder venom and cause less severe symptoms.
| Tarantula Species | Venom Potency | Potential Symptoms in Children |
|---|---|---|
| Poecilotheria (Ornamental Tree Spiders) | High | Severe pain, swelling, nausea, muscle spasms |
| Avicularia (Pinktoe Tarantulas) | Moderate | Localized pain, mild swelling |
| Brachypelma (Mexican Redknee Tarantulas) | Moderate | Moderate pain, swelling, possible mild nausea |
Learning about different tarantulas can help parents know the risks. It also helps them prepare for first aid if a child gets bitten.

Immediate First Aid Steps for Tarantula Bites in Kids
If your child gets bitten by a tarantula, act fast and stay calm. Quick action is key to prevent infection and handle the bite right. Here’s what you should do:
Cleaning and Disinfecting the Bite Area
Start by cleaning the bite area well. Use soap and warm water to wash it. This removes venom or dirt. Then, disinfect with an antiseptic or a damp cloth.
Applying Cold Compresses to Reduce Swelling
To lessen swelling and pain, put a cold compress or ice pack on the bite for 10-15 minutes. This helps shrink blood vessels and reduces swelling. Do this as often as you need to.
Watch your child closely for signs of a bad reaction. Look out for trouble breathing, a lot of pain, or big swelling. If you see these, get medical help right away. Quick action and expert care are key in handling spider bite emergencies for kids.
Tarantula Bite First Aid for Children
If a child gets bitten by a tarantula, acting fast is key. It helps prevent serious problems and helps them get better quickly. You should manage the pain, stop infection, and watch the child closely until they see a doctor.
Start by washing the bite with soap and water. This removes venom and dirt, lowering infection risk. Then, use a cold pack on the bite to ease pain and swelling. Tarantula venom can be strong, so watch for signs like trouble breathing, feeling dizzy, or being sick.
If the child has bad symptoms or a serious allergic reaction, get help right away. Doctors might give them medicine to help with the reaction. This can stop serious problems.
| First Aid Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Wash the Bite Area | Gently clean the bite with soap and water to remove any venom or contaminants. |
| Apply Cold Compress | Apply a cold compress to the affected area to reduce pain and swelling. |
| Monitor for Symptoms | Closely watch for signs of adverse reactions, such as difficulty breathing, dizziness, or nausea. |
| Seek Medical Attention | If the child experiences severe symptoms or shows signs of a serious allergic reaction, seek immediate medical care. |
By doing these Tarantula Bite First Aid for Children steps and watching for any bad signs, parents and caregivers can keep kids safe. Quick and right actions are key to helping the child get better.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
Most tarantula bites in kids can be treated with basic first aid. But, it’s key to know when you need to get emergency help. This ensures your child gets the right care fast.
Signs of Severe Allergic Reaction or Anaphylaxis
Some kids might have a severe allergic reaction or anaphylaxis from a tarantula bite. This is a serious condition that needs quick medical help. Look for these signs:
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Rapid or weak pulse
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Dizziness or loss of consciousness
If your child shows any of these signs, call 9-1-1 or your local emergency number right away. Quick action is key to avoid serious problems.
| When to Seek Emergency Care | Symptoms to Watch For |
|---|---|
| Severe Allergic Reaction or Anaphylaxis |
|
When it comes to spider bite emergency care for kids and managing tarantula bites in youngsters, it’s always best to be cautious. If you’re unsure about your child’s health, get medical help right away.
Preventing Tarantula Encounters with Children
Talking to kids about the importance of respecting tarantula habitats and behaviors can stop accidental meetings and bites. By teaching them about tarantulas, you make them curious and teach them how to stay safe. This way, they learn to appreciate these creatures and know how to avoid dangerous situations.
Teaching Kids About Tarantula Habitats and Behaviors
Begin by telling your kids where tarantulas live, like under rocks or in bushes. Tell them it’s important not to disturb these places because tarantulas might bite if they feel scared. Also, explain how tarantulas are very still and use their looks to hide from predators.
- Explain that tarantulas are generally not aggressive unless provoked or feeling threatened.
- Teach children to observe tarantulas from a safe distance and avoid attempting to touch or handle them.
- Encourage your kids to report any sightings of tarantulas to responsible adults or local authorities, as this information can help with conservation efforts.
By teaching kids to respect tarantulas and their homes, you help them become caretakers of these amazing creatures. This way, you help prevent the need for Tarantula Bite First Aid for Children and keep kids safe from tarantula bites.
Arachnid Envenomation in Youngsters: Key Considerations
Dealing with tarantula bites in kids requires special care. Their small size and growing immune systems make them more at risk from spider venom.
Different tarantulas have different venom strengths. Studies show that some species in the Americas have very toxic venom. It’s important to know which spider bit a child to give the right care.
Kids may show different signs of a tarantula bite than adults. Some have had severe anemia and other serious reactions. Doctors need to know these signs to help kids.
Quick and right first aid is key for arachnid envenomation in kids. Clean the bite, use cold packs, watch for allergic reactions, and know when to call for help. This can really help.
Healthcare workers and caregivers need to understand the special issues with managing tarantula bites in youngsters. Being alert, following the right first aid steps, and getting medical help fast are important. These actions help protect kids from spider bites.
Managing Pediatric Spider Bite Anxiety and Trauma
A tarantula bite can be very scary for a child, leading to a lot of anxiety and fear. As a parent or caregiver, it’s key to offer kind support and advice. This helps your child deal with their feelings and feel safe again.
It’s vital to accept your child’s feelings about the spider bite. Tell them it’s okay to be scared and that their feelings make sense. Let them share their feelings in ways they like, like drawing, writing, or talking to someone they trust.
Also, try relaxation techniques and stress-management methods to help your child after the bite. Deep breathing, guided imagery, or art therapy can lessen anxiety and help them heal emotionally. If your child’s feelings don’t get better or affect their daily life, get help from a mental health expert.