Black Widow Spider: Facts About Venomous Arachnids

The black widow spider is known for its black color and red hourglass mark. These spiders are part of the Latrodectus genus. They are found in North America and have venom that can be deadly to humans.
It’s important to know how to spot them and what to do if bitten. This knowledge helps keep you safe from these dangerous spiders.
Latrodectus: The Infamous Black Widow Genus
The Latrodectus genus includes several widow spider species. The black widow (Latrodectus mactans) is the most feared. They have shiny, jet-black bodies and a red hourglass on their bellies. Other species, like the brown widow and northern widow, look similar but have slight color differences.
All widow spiders have powerful venom. They should be treated with caution.
Identifying Features and Species Overview
The Latrodectus genus, also known as widow spiders, is very venomous. They have shiny black bodies and the famous red hourglass on their bellies. The black widow is the most famous, but other species like the brown widow and northern widow look similar but have different colors and patterns.
- Black widow spiders (Latrodectus mactans) – Jet-black bodies with a prominent red hourglass marking on the abdomen
- Brown widow spiders (Latrodectus geometricus) – Brown or tan bodies with a red hourglass marking
- Northern widow spiders (Latrodectus variolus) – Black bodies with a red, orange, or yellow hourglass marking
All Latrodectus species are very venomous. They should be treated with caution because of their strong venom.

| Species | Coloration | Hourglass Marking |
|---|---|---|
| Black Widow (Latrodectus mactans) | Jet-black | Prominent red hourglass |
| Brown Widow (Latrodectus geometricus) | Brown or tan | Red hourglass |
| Northern Widow (Latrodectus variolus) | Black | Red, orange, or yellow hourglass |
Neurotoxic Venom: A Potent Biochemical Arsenal
The black widow spider’s venom is very powerful. It has a mix of neurotoxins that can be deadly to humans if not treated quickly. The main toxin, alpha-latrotoxin, messes with nerve synapses. This causes muscle pain, breathing problems, and sometimes paralysis.
Even though black widow bites are rarely deadly with fast medical help, their venom is very dangerous. The venom of black widow spiders is made up of many neurotoxins and other active compounds. Each one helps the spider catch its prey, just like the Brazilian Wandering Spider uses its venom to subdue its own prey.
| Venom Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Alpha-latrotoxin | The primary neurotoxin that disrupts neurotransmitter release at nerve synapses, leading to muscle paralysis and respiratory distress |
| Latrodectus toxins | Additional neurotoxins that contribute to the overall spider toxicity and venom potency |
| Proteolytic enzymes | Enzymes that aid in the digestion and liquefaction of the prey’s tissues |
| Hyaluronidase | An enzyme that helps to spread the venom through the victim’s tissues |
The mix of neurotoxins and other compounds in black widow spider venom is very dangerous. It can quickly knock out and control the spider’s prey.
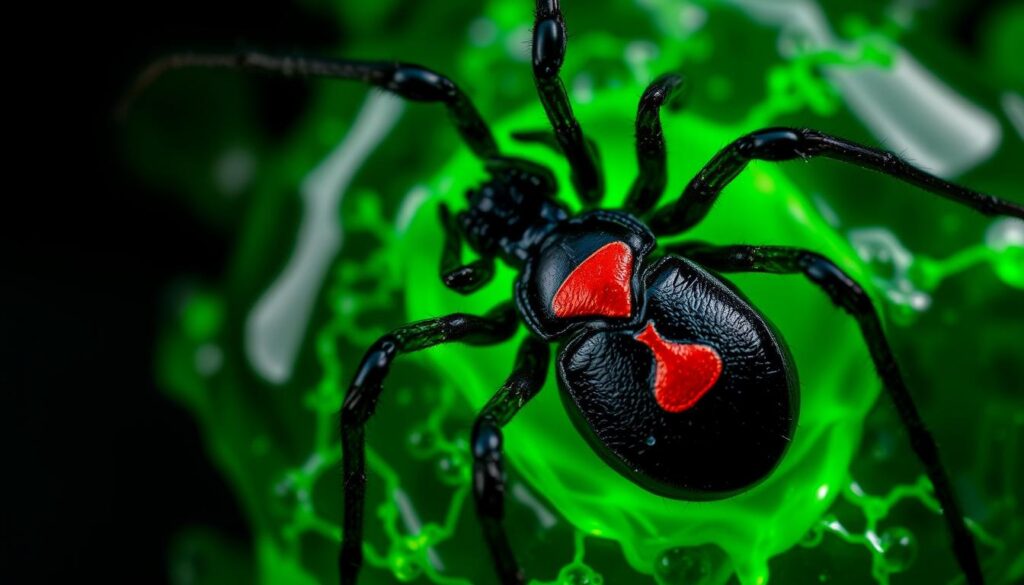
The Black Widow’s Iconic Hourglass Marking
The black widow spider is known for its bright red hourglass on its belly. This sign warns of its dangerous venom. But, the black widow spider markings and coloration patterns can change based on the spider and where it lives.
Variation in Coloration and Patterns
Some black widows are all black, while others have red or white color variations. Young black widows look different from adults. Yet, the hourglass shape is the key sign of these venomous arachnids.
 Black Widow Spider vs. Tarantula: Arachnid Showdown
Black Widow Spider vs. Tarantula: Arachnid Showdown
About 30 black widow spider species are known for their hourglass pattern. The most common in North America is the Latrodectus mactans. Female Latrodectus mactans are about 1 cm long. Other species like L. hesperus, L. variolus, and L. geometricus are found in the U.S. too.
The black widow spider is easy to spot, no matter its color. Its unique look warns people to stay away.
Black widow spider
The black widow spider is a well-known, venomous arachnid in North America. It has a black body and a red hourglass shape on its belly. These spiders have a strong venom that can be dangerous to humans if not treated right.
It’s important to know how to spot a black widow spider to stay safe. They are 1.5 to 3.5 inches long, with females being bigger than males. Their shiny black bodies and red hourglass mark are easy to spot.
- The black widow’s venom is very strong, with a toxin called alpha-latrotoxin.
- Black widow bites are rare but can cause serious symptoms like muscle pain and nausea. In some cases, they can lead to breathing problems or paralysis.
- If you think you’ve been bitten by a black widow, get medical help right away. Quick treatment can reduce health risks.
Knowing about the black widow spider’s unique features and dangers helps us stay safe. We can avoid them and keep ourselves safe in areas where they might be found.
Silk Web Spinning: An Intricate Arachnid Artistry
Black widow spiders are experts at spinning webs to catch their prey. Their webs look messy but are actually very complex. They are hard for insects and small animals to get through.
Web Architecture and Hunting Tactics
Black widows feel when their web vibrates. This tells them when prey is nearby. They then bite their prey with venom, using their web skills to hunt.
The black widow’s web shows off its amazing artistry. It spins a web that looks messy but is actually very smart. This web traps prey, showing the spider’s clever hunting ways.
- Black widows use their web’s vibrations to detect the presence of potential prey.
- Once a victim is detected, the spider quickly strikes, delivering a potent venomous bite.
- The black widow’s web-spinning skills and hunting tactics are crucial to its successful predatory lifestyle.
| Web Spinning Ability | Hunting Tactics |
|---|---|
| Intricate, three-dimensional web structure | Detecting prey through web vibrations |
| Disorganized, tangled appearance to trap prey | Quickly subduing prey with venomous bite |
The black widow’s silk web spinning and hunting behavior are amazing. They help this spider be a top predator. Its web and senses make it a powerful hunter in nature.
Geographical Distribution and Preferred Habitats
The black widow spider (Latrodectus) is found all over North America. It goes from southern Canada to the southwestern United States and parts of Central America. They love warm, dry places and spots where they can hide and find food.
Black widows like to stay in quiet outdoor spots, like under rocks and logs. They also like dark places like woodpiles, sheds, and barns. This is especially true in cities and suburbs where these places are common.
| Region | Habitat |
|---|---|
| North America |
|
| Central America |
|
Knowing where black widow spiders live helps you stay safe. By understanding their habitat and geographic range, you can avoid them. This way, you can keep safe from these venomous arachnids.
Lifecycle and Reproductive Behaviors
The black widow spider, known scientifically as Latrodectus, has a life cycle from egg to adult. Females lay their eggs in intricate silken sacs, which can hold hundreds of eggs. The baby black widows, or spiderlings, hatch and go through molts to grow into adults.
 What are the differences between the black widow and the tarantula?
What are the differences between the black widow and the tarantula?
During their early stages, black widow spiderlings may eat their siblings. As they grow, they go through a unique mating ritual. The female may eat the male after mating. This gives her extra nutrients for her egg sacs.
The time it takes for black widows to mate varies. It can be just a few seconds or several hours. Some males can mate with the same female multiple times. But, the male spiders often die soon after or during mating.
In some cases, the male black widow may leave an epigynal plug after mating. This plug stops the female from mating again. The female’s mating behavior can vary. Some mate only once, while others mate with the same male or multiple males.
| Lifecycle Stage | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Egg Sac | Females lay hundreds of eggs in intricate silken sacs |
| Spiderling | Newly hatched spiderlings undergo a series of molts to reach adulthood, with potential cannibalism among siblings |
| Mating | Unique mating rituals, including sexual cannibalism where the female may consume the male after copulation |
Dangerously Venomous: Treating Black Widow Bites
Symptoms and First Aid Measures
Black widow spider bites are serious because of their strong venom. They can cause muscle pain, nausea, and trouble breathing. In some cases, they can even lead to paralysis.
The venom has alpha-latrotoxin, a toxin that messes with the nervous system. If you think you’ve been bitten, get help right away.
While waiting for help, here are some steps you can take:
- Clean the bite with soap and water to remove venom.
- Use a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain.
- Keep the person calm and still to stop the venom from spreading.
- Watch their breathing and be ready to do CPR if needed.
For serious bites, especially in cats, antivenom is often needed. It’s crucial to get medical help fast to avoid serious problems.
Black widow bites are rare but serious. They can be deadly if not treated right away. Knowing the symptoms and taking the right steps can help keep someone safe.
Widow Spider Control and Prevention Strategies
Keeping your home and family safe from black widow spiders is key. You need a mix of steps, like sealing holes and using pesticides or natural repellents.
Start by checking and cleaning spots where spiders might nest. Remove webs and egg sacs, as one sac can hold hundreds of baby spiders. Vacuuming gets rid of spiders and their eggs, stopping more from coming.
- Seal any openings and cracks in your home’s exterior to deny black widow spiders easy access.
- Use mesh screens in vents and other openings to deny entry.
- Regularly dust and vacuum to eliminate potential hiding spots and food sources.
- Consider using natural repellents like essential oils, vinegar, or chestnuts to deter spiders.
When you’re in areas where black widows might be, wear gloves and long sleeves. Knowing how to spot and treat black widow bites is also important.
If you have a big problem or aren’t sure what to do, call a pest management pro. They know how to get rid of black widow spiders safely and keep your home safe.
Cultural Significance and Mythology
The black widow spider has a big role in culture and myths. It’s seen as a sign of danger, female power, and even sexism. Its scary look and ability to eat its male mates make it famous in stories and movies.
 Why are black widow spiders so deadly?
Why are black widow spiders so deadly?
In many cultures, the black widow spider means different things. It stands for female strength and sex, and the power of nature. It’s also linked to rebirth, change, and life and death cycles, showing our complex bond with nature.
Black widows are important in science and nature, but they also grab our attention. They remind us of the amazing and scary world of spiders. Learning about the black widow spider’s role in myths and culture helps us understand these fascinating creatures better.



